The Analytics feature helps merchants to quickly analyze their transactions within PostFinance Checkout and get insights into their business performance. With structured access to their data, they can predict how to adapt to customer needs. Reports can be customized by writing SQL queries, and all data analysis is powered by PrestoDB, an open-source SQL query engine provided by Amazon Athena.
The Analytics Schema describes the data structures exported from the main PostFinance Checkout database, which can be queried in Portal UI and REST API.
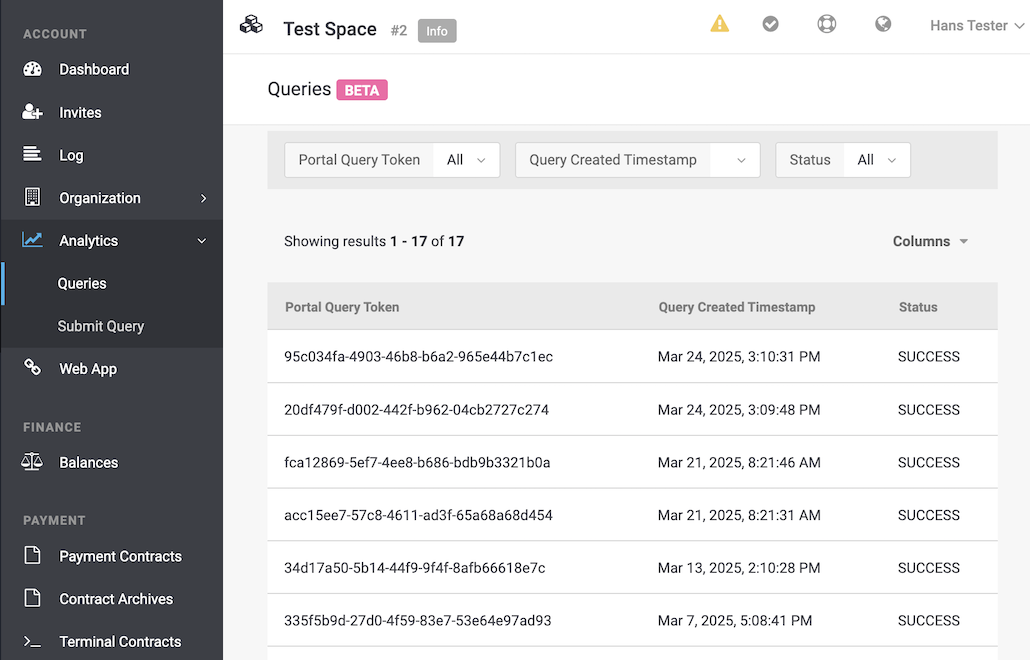
The overview of all analytics query executions can be accessed within the account under Account > Analytics > Queries.

The merchant can submit a query within the specific merchant’s account under Account > Analytics > Submit Query.
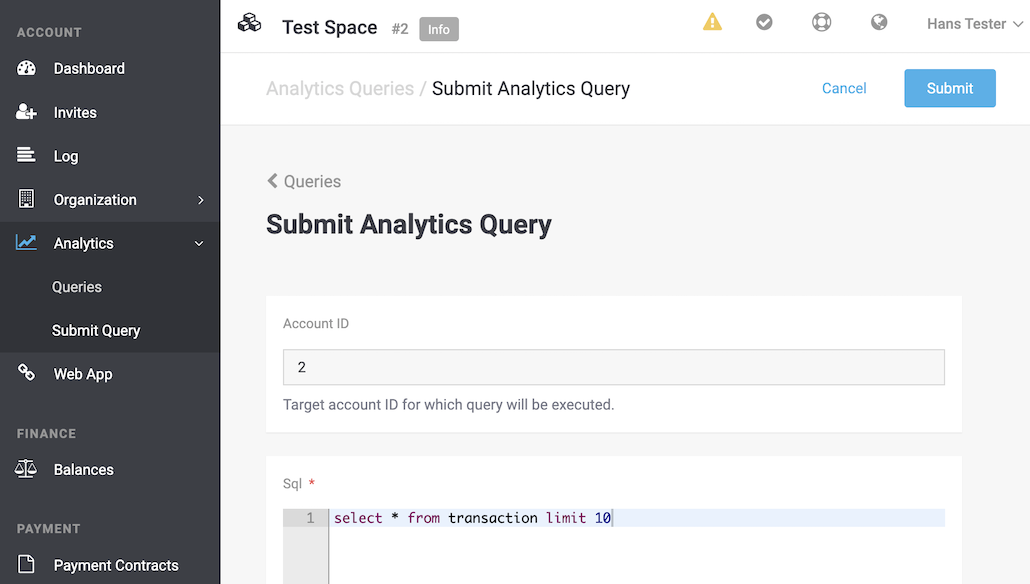
Submit button.A submitted query is processed asynchronously.
Initially, the query execution will have a PROCESSING status, and no details will be available.
Once the query execution is processed and completed, the status will change to SUCCESS and the query details can be retrieved.
If the query execution fails or is canceled before completion, the status will change to FAILED or CANCELLED, respectively, and no detailed query information will be available.
For the restrictions on submitting the query, refer to Access Control and Permissions.
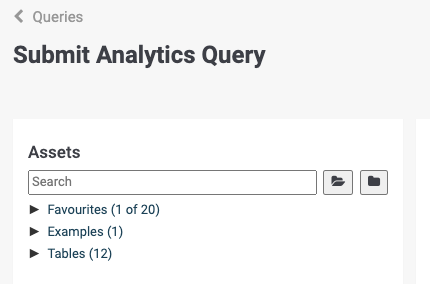
The left side of the query editor features the Assets Panel, a centralized hub for discovering and managing your data. This panel displays:
-
Available Tables: A list of tables and views accessible to you (based on your user permissions), ordered alphabetically.
-
Favorites: A curated collection of saved queries for quick access.
-
Examples: A collection of example queries that can be used as inspiration.
-
Permissions Awareness: Tables are automatically filtered based on your access rights.
To schedule analytics queries for regular execution, use the Recurring Query feature.
Step 1: Create a Recurring Query
-
Navigate to: Account > Analytics > Recurring Queries
Step 2: Configure Query Permissions
-
Recurring queries inherit permissions from the User ID assigned to the query. This ensures consistent access to data for both real and application user types.
-
Important: The User ID determines the security context for query execution.
Step 3: Define the Start Date
-
The Start On date specifies when the query will begin running & click on Create.
-
Note: A valid schedule plan must be set up in the next step for the query to execute.
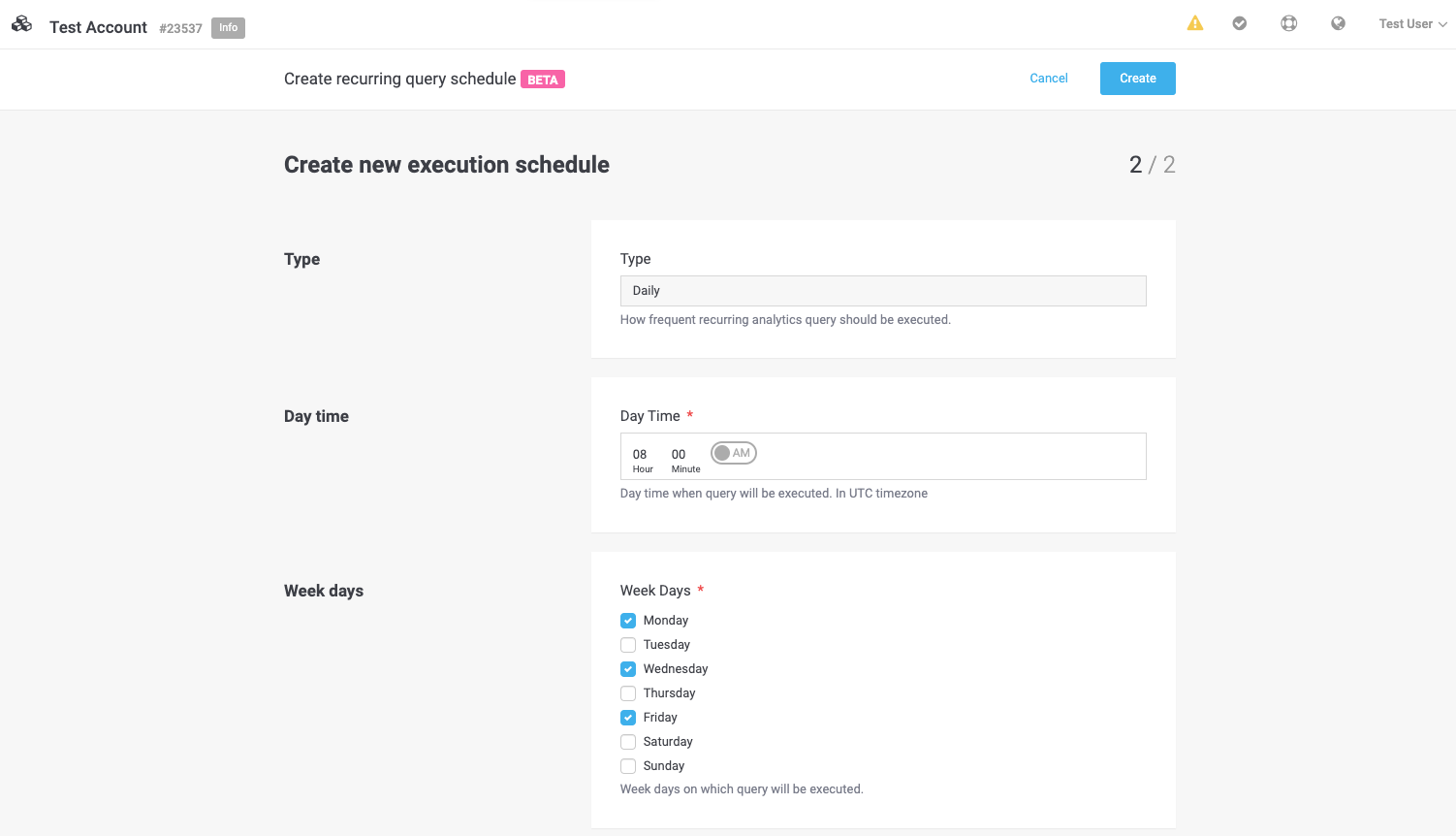
Step 4: Define the Execution Schedule
-
Executes the query at a specified time on defined weekdays.
-
Example: Run every Monday at 9:00 AM.
Visual Reference:
-
Executes the query at a specified time on defined days of the month.
-
Example: Run on the 15th of every month.
Visual Reference:
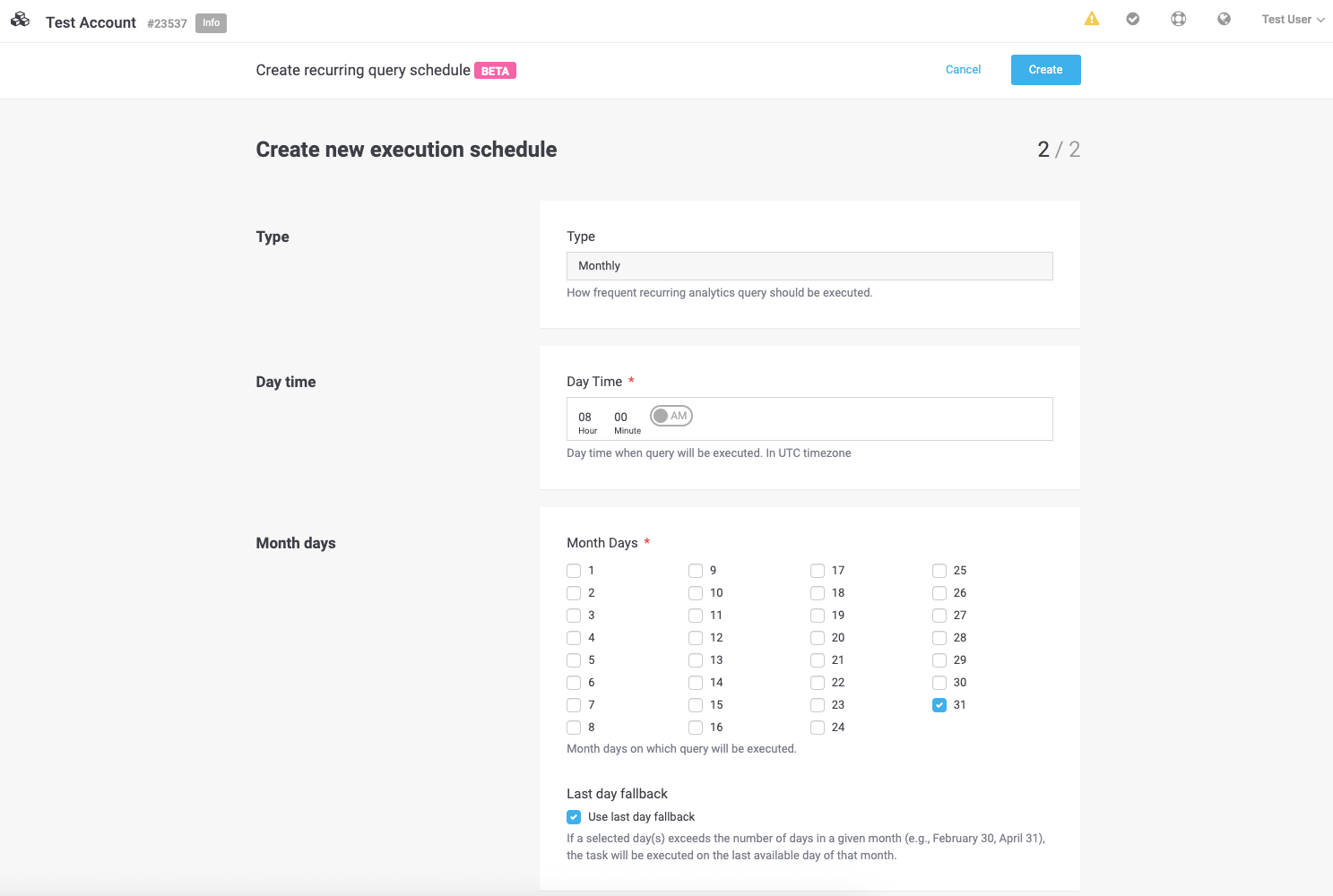
Last Day Fallback:
If your query requires execution on the last day of the month, use this feature:
-
Select 31st as the day.
-
Check the "Use last day fallback" option.
-
The query will automatically adjust to run on the last valid day of shorter months (e.g., February 28th, April 30th).
-
Visual Reference:
-
Consistent Permissions: Recurring queries operate under the same security context as user accounts, ensuring data access aligns with your organization’s policies.
-
Flexible Scheduling: Daily and monthly options allow precise control over when queries run, with fallback logic to handle edge cases like shorter months.
-
Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks to save time and reduce manual effort.
Opening a specific query execution will display the detailed information, including the submitted query SQL request, a download link to the Result File (in CSV format), and available actions for the query (e.g. canceling the query execution).
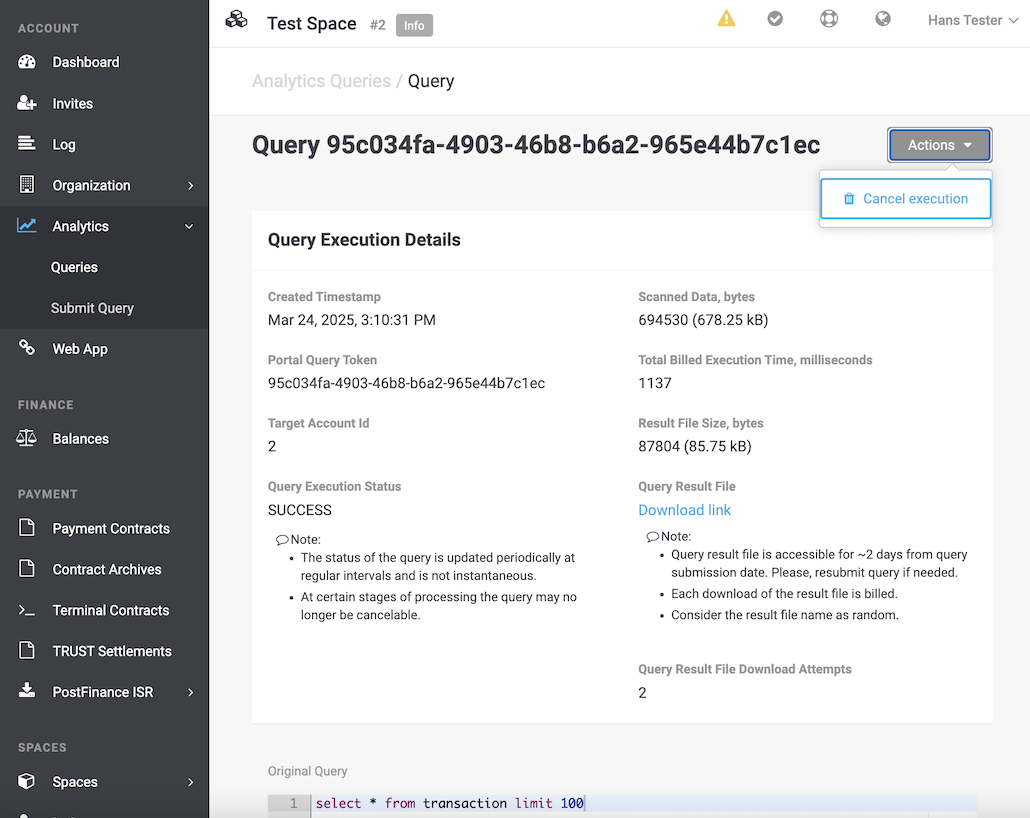
A query execution in PROCESSING status can be canceled by clicking the Cancel execution button from the query execution detailed view page Query Execution Details.
If the query execution has already reached a final status (SUCCESS, FAILED, or CANCELLED), the cancellation attempt will be ignored.
The Analytics Queries REST API is used to manage the execution of Analytics queries.
It allows users to submit query requests, retrieve results in CSV format, monitor query execution, and cancel running queries.
For the complete API reference, see the Analytics Queries REST API documentation.
In this example, a query is executed to list customers ordered by the amount they spent in the merchant’s space. Using the Analytics Schema, we construct the following PrestoDB SQL query, which calculates the sum of transaction amounts grouped by customer:
SELECT SUM(completedamount) AS total, customerid
FROM transaction
GROUP BY customerid
ORDER BY total DESC;|
Note
|
The user must specify table and column names in lowercase, as they are stored internally in lowercase, even though SQL keywords, clauses, and reserved keywords (such as SELECT) are case-insensitive.
|
A query request can be submitted for execution using the Submit Query Execution Request method (HTTP POST).
The request body should contain an Analytics Query Execution Request structure in JSON format.
To submit our example query, we send the following JSON:
{
"accountId": 2,
"sql": "SELECT SUM(completedamount) AS total, customerid FROM transaction GROUP BY customerid ORDER BY total DESC"
}The query request will be executed within the account with ID 2 (specified in the accountId parameter).
The actual SQL query is provided in the sql parameter.
For more details, refer to Access Control and Permissions.
The response for a submission request will be an Analytics Query Execution Response structure in JSON format, containing the queryToken of the execution:
{
"queryToken": "4d135f47-8c13-4b51-86ce-08c5d0f33a00"
}A submitted query is processed asynchronously.
Initially, the query execution will be in PROCESSING status, and no results will be available.
Once the query execution is processed and completed, the status will change to SUCCESS and the query results can be fetched.
If the query execution fails or is canceled before completion, the status will change to FAILED or CANCELLED, respectively, and no results will be returned.
The current status of a previously submitted query can be checked using the Query Execution Status API method (HTTP GET) with queryToken set as a URL path parameter (use queryToken you obtained from your initial call to Submit the Query Execution).
The response of the call to the Query Execution Status method will be a Submitted Query Execution structure. In our example, the request URL will look like this:
/api/v2.0/analytics/queries/4d135f47-8c13-4b51-87ce-08c5d0f33a00Once the query execution reaches the SUCCESS status, a response similar to the following will be received:
{
"accountId": 2,
"createdTimestamp": "2025-03-21T07:56:56.110252Z",
"downloadRequests": 0,
"originalQuery": "SELECT SUM(completedAmount) AS total, customerId FROM transaction GROUP BY customerId ORDER BY total DESC",
"portalQueryToken": "4d135f47-8c13-4b51-87ce-08c5d0f33a00",
"resultFileBytes": 1476198,
"scannedBytes": 763075,
"status": "SUCCESS",
"totalBilledExecutionTimeMs": 1295
}|
Note
|
This Query Execution Status is a long-running request, with a maximum timeout of approximately
|
A query execution in PROCESSING status can be canceled using the Cancel Query Execution method (HTTP DELETE).
Include the queryToken from Submit the Query Execution response.
The request URL will look as follows:
/api/v2.0/analytics/queries/4d135f47-8c13-4b51-87ce-08c5d0f33a00Canceling a query execution will always return an empty response unless there is an error.
If the query execution has already reached a final status (SUCCESS, FAILED, or CANCELLED), the cancellation attempt will be silently ignored.
Once the Query Execution Status returns a SUCCESS status, the query execution results can be retrieved by calling the Query Execution Result API method (HTTP GET request).
Include the queryToken from the Submit the Query Execution response.
The request URL will look as follows:
/api/v2.0/analytics/queries/4d135f47-8c13-4b51-86ce-08c5d0f33a00/resultThe response body contains a temporary Amazon S3 URL (valid for approximately 5 minutes), similar to the following:
https://...s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/query-results/72aaf6a7-86eb-49bb-bded-5ef34e79385b.csv?X-Amz-Security-Token=[...]&X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20250321T082449Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Credential=[...]&X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Signature=[...]|
Note
|
The Query Execution Result method generates a short-lived URL (valid for 5 minutes) for the Analytics Query result file. Each download of the output file incurs a charge, and we also count each file URL generation as a potential download attempt. Please, DO NOT use this API method for periodic checks of the result file availability - use Query Execution Status for periodic checks instead.
|
The availability of tables and data is governed by user roles, which are configured by your Account Admin. These roles determine what data users can access and what actions they can perform.
Example:
-
If a user does not have read access to the transactions table, it will not appear in the Assets Panel, and any query attempting to reference it will fail.
-
Similarly, queries executed in spaces not associated with the user’s account will result in a permission error, as access is restricted to the spaces the user can access.
Key Considerations:
-
Role-Based Access: Permissions are tied to user roles, ensuring data security and compliance.
-
Account-Level Control: Account Admins manage role assignments to control who can access specific tables, views, or datasets.
Need Access Changes?
If you require access to additional tables, datasets, or workspaces, please consult your Account Manager. They can assist with adjusting permissions to align with your needs.
